How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone maneuvers. Mastering drone operation isn’t just about pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to safety regulations, and developing a keen sense of spatial awareness. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently take to the skies, whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced techniques and essential safety protocols.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, providing a clear understanding of how each part contributes to the overall functionality. We will also delve into essential pre-flight procedures, ensuring a safe and responsible flight every time. Learning to control altitude, direction, and speed smoothly is crucial, and we’ll guide you through this process with step-by-step instructions and helpful tips.
Finally, we’ll discuss the legal and ethical aspects of drone operation, emphasizing responsible and safe flying practices.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section provides a breakdown of key components and a glossary of common drone terminology.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the interplay of several key components. Each plays a vital role in its ability to fly and perform tasks.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and maneuver. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. The speed and direction of these motors are controlled by the flight controller.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, the flight controller receives input from various sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and GPS) and uses this data to regulate motor speed and maintain stability. It also processes commands from the remote controller.
- Battery: The power source for the drone, providing energy to the motors and other electronic components. Battery capacity and voltage directly impact flight time and performance.
- GPS Module (optional): Many drones incorporate a GPS module for precise positioning and autonomous flight functions. This allows for features like waypoint navigation and return-to-home functionality.
- Camera (optional): Many drones include a camera for aerial photography and videography. Camera features vary significantly, with some offering high resolution, image stabilization, and other advanced capabilities.
- Remote Controller: The device used to pilot the drone and control its camera. It transmits signals to the flight controller, enabling the user to control the drone’s movement and functions.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology is essential for understanding manuals, online resources, and discussions about drone operation.
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Altitude Hold | The drone maintains a constant altitude above the ground. | Useful for stable aerial photography. |
| Gimbal | A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing vibrations and ensuring smooth footage. | Essential for high-quality video recording. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | A function that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point. | Important safety feature in case of signal loss. |
| Waypoint | A pre-programmed location that the drone navigates to autonomously. | Used for creating complex flight paths. |
Drone Battery Comparison
Different drone batteries offer varying capacities, voltages, and flight times. Choosing the right battery depends on your flight needs and drone model.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Battery A | 1500 | 11.1 | 20-25 |
| Example Battery B | 2200 | 14.8 | 30-35 |
| Example Battery C | 3000 | 15.2 | 40-45 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone for any damage, verifying battery charge, and checking the surrounding environment.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, follow these steps to minimize risks:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or body.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is adequately charged.
- Verify the GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Confirm that the remote controller is fully charged and properly connected.
- Assess the surrounding environment for potential hazards (obstacles, people, weather).
- Check local regulations and ensure you are complying with them.
- Calibrate the drone’s sensors according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight range test to check the connection between the drone and controller.
Pre-Flight Inspection for Damage
A careful visual inspection is crucial to identify any potential problems before flight. Pay close attention to propellers for cracks or bends, check the motor mounts for looseness, and examine the drone’s body for any signs of damage.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure helps streamline the process and ensure no steps are missed. A flowchart would typically show a sequential process starting with a battery check, proceeding to a visual inspection, then confirming GPS signal and regulatory compliance, before finally performing a pre-flight calibration and range test.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. These procedures minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the longevity of your equipment.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone This website offers comprehensive guidance on various aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace restrictions. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Takeoff and landing should always be performed in a clear, open area, away from obstacles and people. Consider wind conditions; avoid windy conditions for novice pilots. Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times during takeoff and landing. Use a smooth, controlled approach to avoid abrupt movements.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Assisted takeoff utilizes the drone’s automatic features (like altitude hold) to aid in a smoother, more controlled ascent. Manual takeoff involves more direct control over the drone’s movements. The choice depends on pilot skill and environment.
Maintaining Visual Line of Sight
Keeping the drone within your direct line of sight is crucial for safe operation. This allows you to react to any unexpected events and maintain control of the aircraft. Losing visual contact can lead to accidents or loss of the drone.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Mastering basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section details how to control altitude, direction, and speed, and Artikels common maneuvers.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
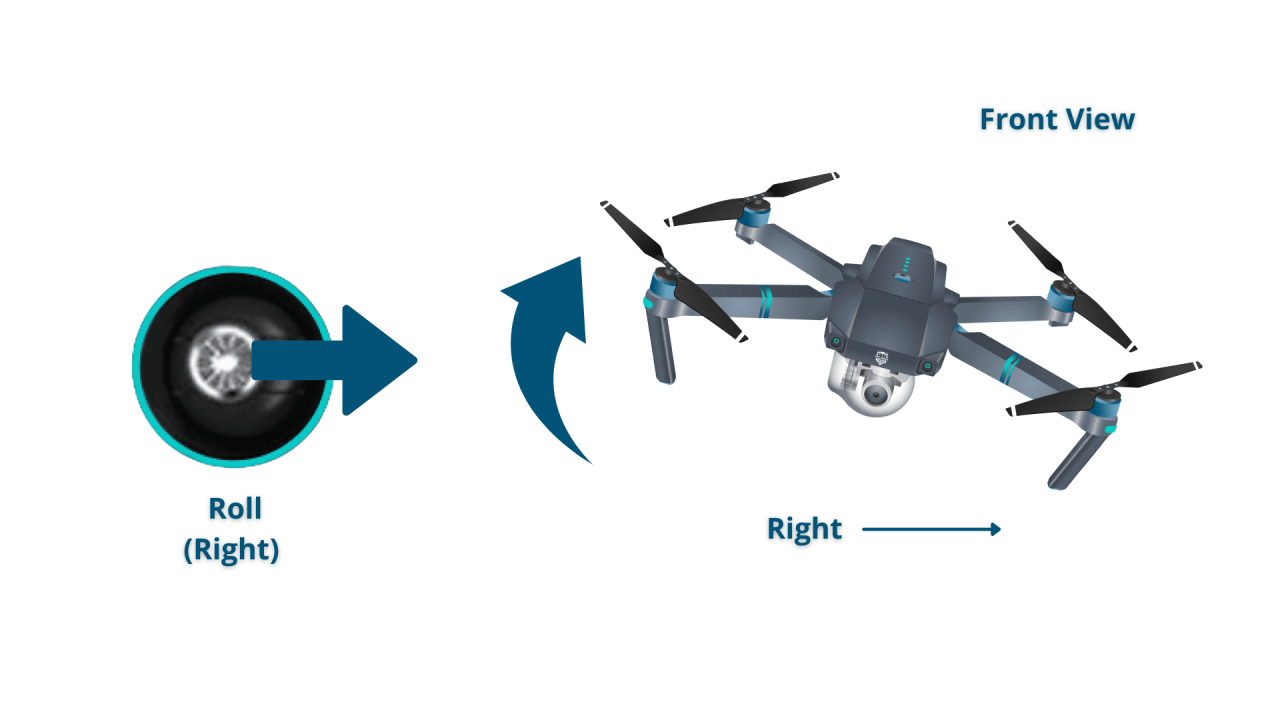
Most drone controllers use joysticks to control the drone’s movements. One joystick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement. Throttle controls altitude, while directional inputs adjust heading and lateral movement. Speed is often adjustable through settings on the controller or within the drone’s flight app.
Basic Maneuvers
Hovering involves maintaining a stable position in the air. Turning involves rotating the drone around its vertical axis. Moving forward, backward, and sideways involves controlling the directional inputs on the controller. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Sudden, jerky movements of the controller.
- Ignoring wind conditions and flying in strong winds.
- Not maintaining visual line of sight.
- Flying too close to obstacles.
- Ignoring battery level warnings.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques, such as waypoint navigation and autonomous flight, expand the drone’s capabilities. However, these techniques require careful planning and adherence to safety precautions.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight
Waypoint navigation allows you to program a series of points for the drone to follow autonomously. Autonomous flight features, like “follow me” or “point of interest,” utilize GPS and other sensors to automate certain flight maneuvers. These features offer creative possibilities but necessitate thorough understanding and careful planning.
Safety Precautions for Advanced Maneuvers
Always practice advanced maneuvers in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people. Ensure you have a strong GPS signal and sufficient battery power. Familiarize yourself with the drone’s emergency stop procedures before attempting complex flights.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. From there, practice and experience will further hone your skills in operating a drone safely and effectively.
Flight Mode Comparison
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers. Choosing the appropriate mode depends on your skill level and the complexity of the flight.
| Flight Mode | Speed | Responsiveness | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Low | Low | High |
| Sport Mode | High | High | Moderate |
| GPS Mode | Variable | Variable | High (GPS assisted) |
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Many drones are equipped with cameras capable of capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to achieving high-quality results.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture affect image quality. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions, but can introduce noise. Shutter speed determines motion blur; faster speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create a sense of movement. Aperture controls depth of field; wider apertures create shallow depth of field, while narrower apertures increase depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Use a tripod or gimbal for stable shots. Avoid shooting directly into the sun. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find creative compositions. Keep the drone’s battery level in mind to ensure sufficient recording time.
Composing Compelling Drone Shots
Consider leading lines, rule of thirds, and symmetry to create visually appealing compositions. Experiment with different angles (low, high, side) to create unique perspectives. Pay attention to lighting and shadows to enhance the mood and atmosphere of your shots. Plan your shots in advance to ensure you capture the best possible images.
Drone Safety and Regulations: How To Operate A Drone

Understanding and adhering to drone regulations is crucial for safe and legal operation. This section highlights important safety practices and potential hazards.
Understanding and Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. This typically involves registering your drone, obtaining necessary permits, and adhering to airspace restrictions.
Safe Flying Practices
Always maintain visual line of sight. Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace. Never fly over crowds or in hazardous weather conditions. Be mindful of battery life and always land the drone before the battery is completely depleted.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation
- Obstacles: Always be aware of your surroundings and avoid flying near trees, buildings, or power lines.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow. Adverse weather can affect drone stability and control.
- Signal Interference: Interference from other electronic devices can disrupt the connection between the drone and controller. Choose a location with minimal interference.
- Battery Failure: Always use fully charged batteries and monitor the battery level during flight. Land immediately if the battery is low.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
This section addresses common drone problems and provides solutions to resolve them. A systematic approach to troubleshooting can help you quickly identify and fix issues.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Troubleshooting involves a logical process of elimination to pinpoint the root cause. Start by checking the most obvious factors (battery, signal, physical damage) before moving to more complex issues.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before attempting to fly. Consider using a higher capacity battery for longer flights.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Ensure the GPS module is functioning correctly.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motors for damage. Replace any faulty motors.
- Controller Issues: Check the controller’s batteries and ensure a strong connection with the drone.
- Drone Not Responding: Restart the drone and controller. Check for software updates.
Troubleshooting Guide
This guide provides a structured approach to addressing common issues. Always consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
-
If the drone is unresponsive, try restarting both the drone and the controller. This often resolves temporary software glitches.
-
If you experience GPS signal loss, ensure that you are flying in an open area with a clear view of the sky, away from tall buildings or dense foliage.
-
Low battery warnings should always be heeded. Land the drone immediately to prevent a complete power failure mid-flight.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and best practices for storage.
Regular Maintenance Schedule, How to operate a drone

A regular maintenance schedule should include cleaning the drone after each flight, inspecting for damage, and checking the battery and motors. More thorough inspections should be conducted at regular intervals (e.g., monthly).
Best Practices for Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep the battery separate from the drone to prevent accidental discharge. Use protective cases or containers to shield the drone from dust and damage during storage.
Cleaning and Inspecting After Each Flight
After each flight, gently clean the drone’s body and propellers to remove any dirt or debris. Inspect the drone for any damage and address any issues promptly. This preventative maintenance will ensure your drone remains in optimal condition.
Successfully operating a drone is a rewarding experience that blends technology, skill, and a deep respect for safety regulations. From understanding the mechanics of flight to mastering advanced maneuvers, this guide has provided a solid foundation for your drone journey. Remember that practice is key, so take your time, embrace the learning process, and always prioritize safety. As you gain experience, you’ll discover a whole new perspective on the world from above, capturing stunning visuals and expanding your creative horizons.
Soar responsibly and enjoy the adventure!
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models with positive reviews and consider your budget.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, payload). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a “return-to-home” function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always maintain visual line of sight as much as possible.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
